Understanding crushed stone grades: A complete guide to gravel sizes

Article updated October 10, 2025
Crushed stone and gravel are essential materials in construction and landscaping projects, but understanding the different grades can help you make informed decisions when selecting the right material for your needs. Whether you're laying a base for pavers or creating a gravel driveway, knowing the right crushed stone grade can save time, money, and hassle. In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about crushed stone grades, common uses, and how to select the best option for your project.
When contractors talk about “gravel sizes” or “stone size ranges,” they are really referring to how large each piece of aggregate is after crushing and screening. Understanding these size ranges ensures you can choose the correct base material, drainage layer, or decorative top layer depending on your project type.

What Is Crushed Stone?
Crushed stone is a versatile material made from natural rock deposits that are broken down into smaller pieces using a crusher (find out what a crusher is here). It is graded based on size, with specific numbers indicating the screen size used to sift it. These stones vary in size and are categorized into grades to indicate their size and use. The most common sizes are 8 stone, 57 stone, and 67 stone, but there are many more depending on your project’s needs. Understanding the differences in these grades is crucial in choosing the right material for your project.
Crushed stone is sometimes called aggregate or gravel depending on its source and finish. While crushed stone is mechanically broken, natural gravel is often rounded from riverbeds. Both materials share similar size designations, which can cause confusion when comparing gravel size charts online.

Discover crushers for sale at Machinery Partner
Crushed Stone Grades Explained
The classification of crushed stone is based on its size. Each grade has its own distinct characteristics and uses:
- #1 Stone: This grade consists of the largest particles, ranging from 2-4 inches in diameter. It is ideal for larger construction projects or filling big holes, offering a sturdy and reliable foundation. Because these are larger stones, #1 aggregate is often used as a sub-base in heavy road construction or for erosion control along embankments.
- #3 Stone: These stones are ½-2 inches in diameter and are commonly used in railroad projects and drainage systems, where their size and durability are highly valued. This mid-range gravel size provides strong compaction while still allowing water to pass through, making it a good choice for driveways that require drainage.
- #5 Stone: Measuring 1 inch or smaller, this grade is perfect for road and paver base materials, providing a stable foundation for various types of pavement. It’s also a popular choice for residential driveways and walkways because the smaller particle size creates a smoother surface once compacted.
- #8 Stone: This grade measures approximately 3/8 inch in size and is commonly used in concrete mixes and asphalt. It provides excellent compaction and is ideal for creating smooth surfaces. #8 stone or pea-sized gravel can also be used decoratively in landscaping beds and pathways, thanks to its fine texture and attractive look.
- #10 Stone: Known as screenings or dust, this fine material is used for pavers and concrete blocks, offering a smooth finish and enhancing structural integrity. Stone dust helps lock larger aggregate together and fills air gaps, preventing shifting in patios, walkways, and retaining wall bases. It’s sometimes sold as “crusher run” when blended with larger aggregate.
- #57 Stone: One of the most common and versatile sizes, 57 stone is about ¾ inch in size. It is often used for driveways, drainage solutions, and as a base for concrete and asphalt. It allows for excellent drainage while providing a stable foundation. Because of its balance between drainage and stability, #57 stone is one of the most frequently specified grades for residential and commercial projects alike.
- #67 Stone: Slightly smaller than 57 stone, 67 stone measures around ¾ inch as well but is often used for slab bases and in concrete mixes. Its slightly smaller size allows for more compact surfaces, making it ideal for roads and highways. This grade’s fine-to-medium particle mix makes it an excellent choice when you need smoother compaction without losing strength.
- #411 Stone: A mix of #57 stone and #10 screenings, this grade is ideal for creating a solid, compacted base for construction projects. It’s commonly used under driveways and parking pads as a road-base material. The mixture of coarse and fine aggregate promotes interlocking for superior stability.
Each grade serves a specific function, so knowing the right one for your application ensures that your project will have the durability and performance needed.
If you are unsure which crushed stone size range you need, consult a gravel size chart or talk to an aggregate supplier who can match your project’s specifications.
Types of Gravel
Gravel differs from crushed stone in that it consists of naturally occurring loose stone chunks. Typically smoother and more rounded, gravel offers unique qualities that make it suitable for particular applications in both construction and landscaping.
The most common types of gravel are classified by both their origin (such as river rock or marble chips) and their particle size. Each variation offers different drainage characteristics, surface textures, and aesthetic appeal.
Common Types of Gravel
- Pea Gravel: Small, round stones that are comfortable underfoot and visually appealing, pea gravel is often used for paths, driveways, and garden beds. It requires proper edging to prevent movement and maintain its layout. Because of its small particle size and smooth texture, pea gravel is also a great option for playgrounds or areas where barefoot traffic occurs.
- River Rock: Larger than pea gravel, river rock features smooth, rounded edges and is ideal for landscaping projects, offering a natural aesthetic. However, it is not suitable for driveways without proper edging to keep it in place. Its rounded stones are excellent for decorative borders, water features, or erosion control near drainage swales. Its rounded stones are excellent for decorative borders, water features, or erosion control near drainage swales.
- Lava Rock: Lightweight, porous, and available in red, black, or gray, lava rock is primarily used for landscaping and as mulch due to its water retention properties and unique appearance. It’s particularly valued in arid climates where traditional mulch may dry out quickly, and it adds a bold contrast to surrounding greenery.
- Marble Chips: White and gray stones with a shimmering appearance, marble chips provide a beautiful aesthetic for high-end projects, adding elegance and sophistication to landscaping designs. Marble chips reflect light and heat, which can help keep garden beds cooler during hot months but may require a weed barrier underneath to prevent soil staining.
- Jersey Shore Gravel: Comprising tan, white, brown, and gold stones, this gravel mimics beach sand and is popular in the Mid-Atlantic states for driveways and walkways, offering both style and durability. This decorative gravel is a popular choice in coastal areas where homeowners want a natural, bright look that resists fading and compacts well for vehicle use.

Understanding the Gravel Size Chart
Choosing the right size stone for your project can be made easier by referring to a gravel size chart. These charts offer visual representation and technical specifications for each type of gravel, helping you quickly determine the appropriate grade. For example, #57 stone is known for its ability to compact well while still offering enough space for water to flow through, making it a great choice for drainage and driveway projects.
A comprehensive gravel size chart can help you compare aggregate by particle size, from coarse crushed rock to fine gravel and stone dust. This visual guide allows contractors, landscapers, and DIYers to quickly see which sizes work best for base layers, decorative landscaping, or road construction applications.
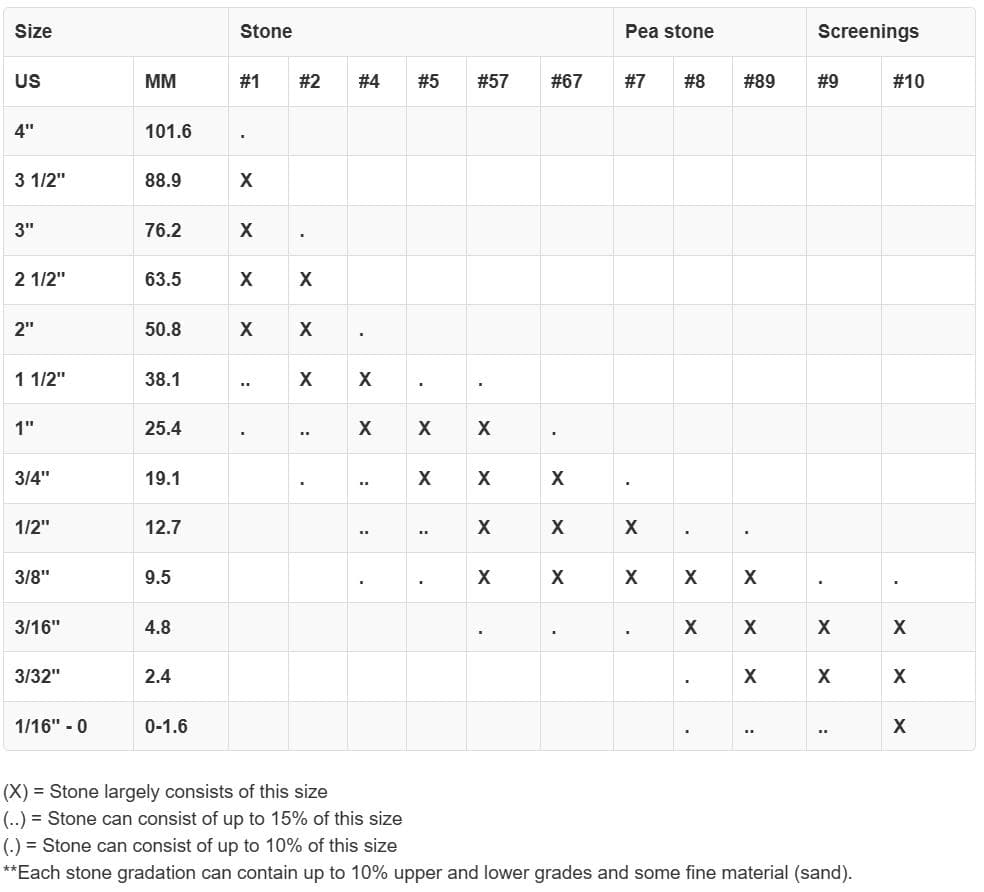
Using a gravel size chart can save you time by showing exactly what each grade looks like and where it’s best used. You can also compare different stone types such as 8 stone and 57 stone to see how they differ in size and application.
For instance, fine gravel under ¼ inch may be ideal for paver joints or finishing layers, while larger stones over 2 inches are better suited for drainage or erosion control.
What Is the Difference Between 8 Stone and 57 Stone?
When comparing 8 stone and 57 stone, the primary difference is size. 8 stone is smaller and used for concrete mixes and thin asphalt layers. It provides smooth surfaces and is ideal for smaller projects. On the other hand, 57 stone is larger and works well for creating solid foundations, backfilling, and drainage solutions. While both offer compaction properties, 57 stone is better suited for larger construction tasks, while 8 stone is ideal for finishing touches and surface layers.
Both types are commonly listed on gravel size charts because they are among the most used grades in residential and commercial construction. 8 stone offers a smoother, decorative finish for landscaping projects, while 57 stone’s coarse texture makes it perfect for driveways and road base layers where durability matters most.
Discover screeners to make DOT approved material at Machinery Partner
#67 Stone vs. #57 Stone: Which Is Better?
The choice between 67 stone and 57 stone depends on the specifics of your project. 67 stone is slightly smaller than 57 stone, making it a good choice for thinner layers of concrete or asphalt. It compacts well and creates a smooth surface. 57 stone, however, is larger and provides better drainage and stability, making it ideal for driveways, foundations, and backfill. Depending on your needs, either stone could work, but understanding their slight differences helps you make the best decision.
Generally speaking, 57 stone is a more versatile material because it balances load-bearing capacity with excellent drainage. 67 stone may be preferred in applications that need a tighter surface finish, such as road shoulders or slab foundations. Both can be combined with screenings to create custom crusher run blends that improve compaction.

Selecting the Right Material
When selecting materials for your project, consider specific requirements such as desired texture, compaction, drainage, and aesthetic goals. For example, #57 stone is an excellent choice for driveways due to its balance between size and drainage properties, providing a durable and long-lasting surface. In contrast, #8 gravel is perfect for decorative landscaping, offering visual appeal without sacrificing practicality.
If you are building a walkway or patio, use smaller stones or screenings as a base layer to ensure tight compaction and prevent shifting. For retaining walls or drainage trenches, larger stones or riprap are better suited to handle water flow and soil pressure. Matching the right stone size to your use case ensures longevity and minimizes maintenance costs.
Common Uses for Crushed Stone Grades
- Paver Base Material: Grades like #57 stone and #8 gravel are commonly used as base layers for paver projects. They provide excellent compaction and drainage, ensuring your pavers stay in place for years. The combination of fine and medium aggregate allows water to drain away while keeping the paver base stable under heavy loads.
- Driveways: For gravel driveways, crushed gravel or 57 stone gravel is often the material of choice. It compacts well, is easy to spread, and provides solid footing for vehicles. Homeowners often prefer this material because it creates a smooth surface that resists rutting and allows rainwater to drain naturally, reducing erosion compared to solid pavement.
- Landscaping: Smaller stones like #8 stone are frequently used in landscaping for decorative purposes or as ground cover for plant beds and pathways. These fine gravels can be used as mulch alternatives, providing weed control and helping soil retain moisture. Their various colors and textures make them a popular choice for decorative landscaping projects.
- Drainage: Larger stones, such as 67 stone and 57 stone, work exceptionally well in drainage applications. Their size allows water to pass through easily, making them ideal for French drains and foundation backfill. In erosion control systems, coarse aggregate helps stabilize slopes and riverbanks, preventing soil loss while maintaining natural water flow.

In addition to these uses, crushed stone and gravel are also vital in road construction, concrete mixes, and retaining wall backfill. Each application benefits from selecting the correct stone size and type based on compaction and drainage needs.
Choosing the Right Crushed Stone Grade for Your Project
When selecting crushed stone, consider the specific needs of your project, such as the desired surface texture, compaction, and drainage. If you're building a driveway, for example, 57 stone is a popular choice due to its balance between size and drainage properties. For decorative landscaping, smaller stones like #8 gravel work well for creating a polished appearance.
For road construction or heavy-duty commercial sites, larger grades like #3 or #5 aggregate create the strength and depth necessary to support heavy equipment. For homeowners building patios or garden walkways, finer materials such as screenings and stone dust ensure a smooth finish that stays compacted over time.
If you need help selecting the best stone for your project, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at Machinery Partner. We offer a wide range of crushers and screeners that can help you achieve the perfect size and grade for your materials.
Crushing and Screening Equipment for Stone Processing
Once you’ve chosen the right crushed stone grade, you’ll need the right machinery to process it. At Machinery Partner, we offer a variety of crushers and screeners designed to handle different types of stone and gravel. From jaw crushers to cone crushers, we have the equipment to help you process materials efficiently, saving time and money. For more information on setting up a crushing plant, visit our blog here.
Processing your own aggregate allows greater control over material costs and quality. Using a crusher and screener setup lets you produce on-spec gravel for driveways, road base, or decorative landscaping projects—all while reducing waste and hauling expenses.

Choose the Right Crushed Stone for Your Project
Find out all about crushing plants, what they are and how you can set one up. Understanding crushed stone grades is essential for any construction or landscaping project. By knowing the differences between grades like 57 stone, 67 stone, and 8 stone, you can select the right material for your specific needs. If you're ready to start making your own on spec crushed stone, contact Machinery Partner today to find the right crushers, screeners, and stone products for your project. Call us at 888-297-0623 or explore our product listings to see how we can help you maximize efficiency and save money.
No matter your project type—whether it’s a gravel driveway, road construction, or decorative landscaping—understanding the various gravel sizes and crushed stone grades can make the difference between a project that lasts and one that requires constant maintenance. This comprehensive guide provides the foundation to choose the right aggregate every time.







