Wood Grinders: A Complete Guide

Wood grinders are essential equipment for turning logs, pallets, brush, stumps, shingles, and wood waste into mulch, compost feedstock, or biomass fuel. Whether you run a sawmill, a land clearing business, or a commercial mulch operation, wood grinders offer the durability, versatility, and throughput needed to process high volumes of material efficiently.
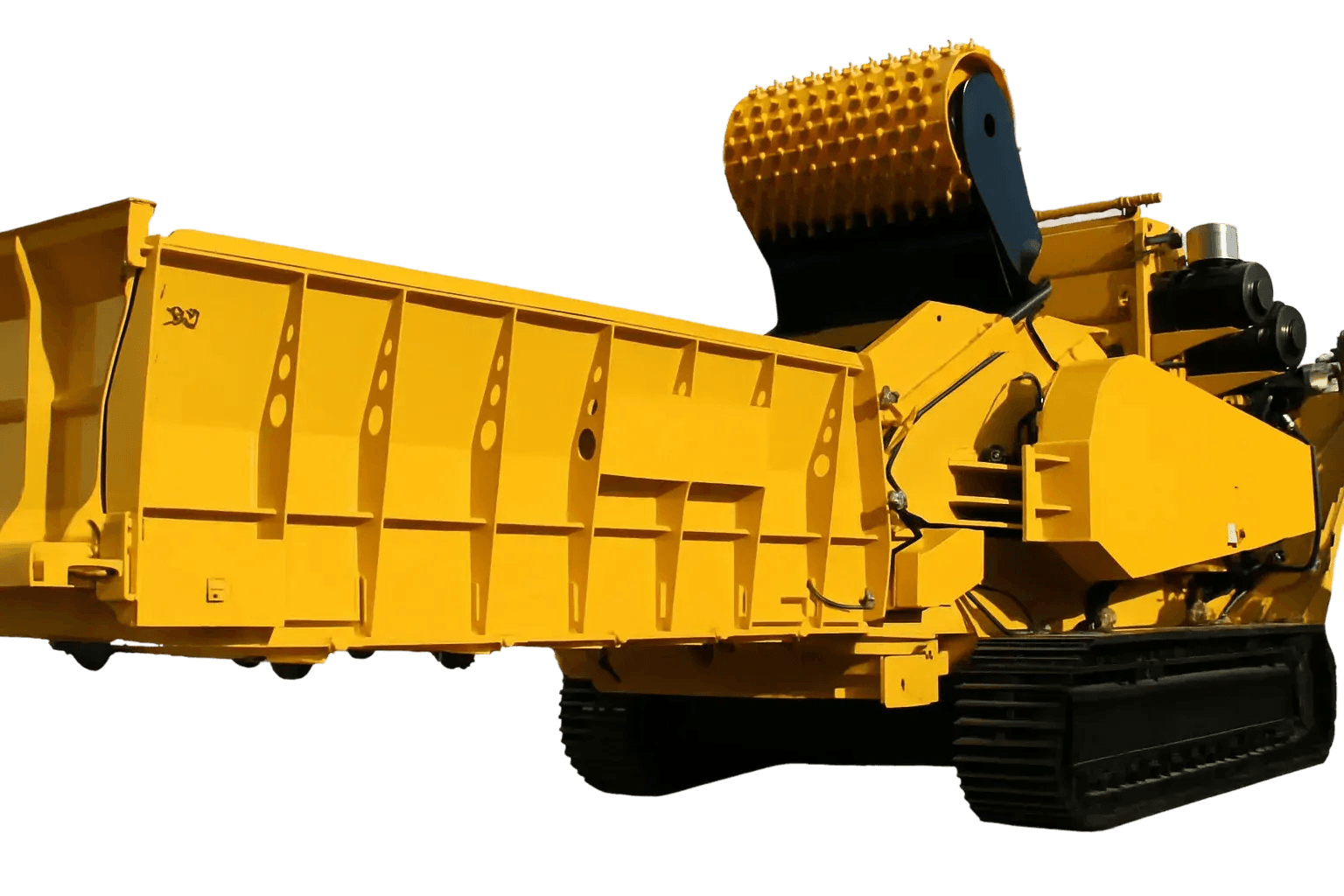
Compared to chippers, grinders use high-speed or variable-speed cutting systems to produce finer, more consistent output. Horizontal grinders, hammermills, and shredders are now standard in wood waste recycling facilities because they handle mixed material streams, contaminated waste, and oversized loads more effectively than older machines.
With the right wood grinder, operators can turn material that would otherwise end up in a landfill into high-value mulch, compost, or renewable biomass—improving sustainability and lowering disposal costs.
What a Wood Grinder Does
A wood grinder reduces raw wood material into chips, fiber, or mulch-sized particles using a rotor equipped with teeth, hammers, or cutting inserts. The grinding action breaks down:
- Pallets
- Brush
- Demolition wood
- Sawmill waste
- Stumps
- Hardwood and softwood logs
- Shingles
- Compost feedstock
Material enters through an infeed system that regulates feed rate to match RPM and torque demands. The grinder produces a consistent final product suitable for mulch production, composting, and biomass fuel.
Types of Wood Grinders
Different grinding systems handle specific material types and production requirements. Understanding these helps operators choose the most cost-effective solution.
Horizontal Grinders
Horizontal grinders are the workhorse of the wood waste industry. They use a horizontal infeed system and a high-speed rotor to process logs, pallets, brush, and even contaminated material. With adjustable screens, operators can produce fine mulch or coarser chips depending on end-use.
Horizontal grinders are ideal for:
- High-volume mulch producers
- Land clearing operations
- Waste handling facilities
- Sawmills with continuous wood waste
Their durability and high production rate make them popular replacements for older hammermills.
Hammermill Grinders
Hammermills use swinging hammers mounted on a central rotor to crush and pulverize wood. They excel at processing:
- Shingles
- Pallets
- Sawmill trim
- Mixed demolition wood
Hammermills create smaller, more uniform particles and are used heavily in composting operations and mid-volume mulch production.
Shredders with Grinder Attachments
Some operations combine shredders for primary size reduction with grinders for finishing. This is common where contaminated wood waste or mixed C&D material must be processed before entering the grinder.
Stump Grinders and Specialty Machines
For stump removal, dedicated stump grinders are used to pulverize hardwood stumps and root balls. While not traditional “wood grinders,” they support land clearing operations by freeing material for secondary grinding or disposal.
Key Features of a Wood Grinder
Several core features determine performance, throughput, durability, and versatility.
Rotor and Cutting System
The rotor drives grinding action, and its design influences RPM, aggressiveness, and chip uniformity. Heavy-duty rotors handle hardwood logs and stumps, while more flexible cutters handle shingles or pallet waste.
Variable Speed Control
Variable feed speed helps match material hardness and size to grinder capabilities. This improves fuel efficiency, reduces wear, and increases operator control.
Infeed System
A high-quality infeed controls material flow into the cutting chamber. Systems may include:
- Conveyors
- Rollers
- Feed chains
- Dual infeed systems for high-volume operations
Screens and Sizing Control
Screens regulate the final particle size. Smaller screens produce fine mulch; larger screens produce chips for compost or biomass applications.
Engine and Power Options
High-RPM diesel engines are standard. Larger grinders rely on heavy-duty engines capable of handling hardwood, stumps, and large-diameter logs without bogging down.
Common Applications Across Wood Waste and Recycling
Wood grinders are used across many segments in the wood waste and environmental industries.
Mulch Production
Horizontal grinders and hammermills produce consistent, sellable mulch from logs, brush, and pallets. Operators can fine-tune output particle size using different screens.
Composting Operations
Compost facilities use grinders to break down organics into a uniform material that decomposes efficiently.
Land Clearing and Forestry
Land clearing contractors rely on grinders to reduce brush, logs, and stumps into chips for haul-off or onsite reuse.
Sawmills
Sawmills use grinders to turn slabs, trim, and offcuts into usable biomass or mulch.
Shingle Recycling
Hammermill-style grinders handle asphalt shingles and produce consistent output for reuse and recycling.
Benefits of Using a Wood Grinder
Wood grinders offer significant productivity, environmental, and cost advantages.
- Consistent mulch and compost-size output
- Ability to grind pallets, shingles, and contaminated waste
- High durability and heavy-duty design for continuous production
- Variable speed options to match different materials
- Reduced landfill tipping fees
- Revenue from mulch, compost, and biomass sales
- Versatility to process hardwood, brush, and mixed waste
High-speed grinders like those found in commercial mulch operations can process large volumes with extraordinary efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wood Grinders
What is the difference between a wood grinder and a wood chipper?
Chippers produce uniform chips using knives; grinders use a rotor and hammers to create smaller mulch-like particles and handle more diverse material streams.
What kind of grinder should I use for mulch production?
Horizontal grinders and hammermills are ideal due to their fine output, high throughput, and ability to handle mixed wood waste.
Can a grinder handle stumps and hardwood?
Yes. Heavy-duty grinders with robust rotors and high horsepower can process hardwood and stumps effectively.
Do wood grinders work for compost operations?
Yes. Grinders produce small, uniform particles that break down efficiently in composting systems.
How do screens affect final product size?
Screens determine output material size. Smaller screens create finer mulch; larger screens produce coarse chips.
What RPM do wood grinders operate at?
RPM varies by grinder size and rotor design, but high-speed grinders typically operate at several thousand RPM to achieve consistent grinding action.






